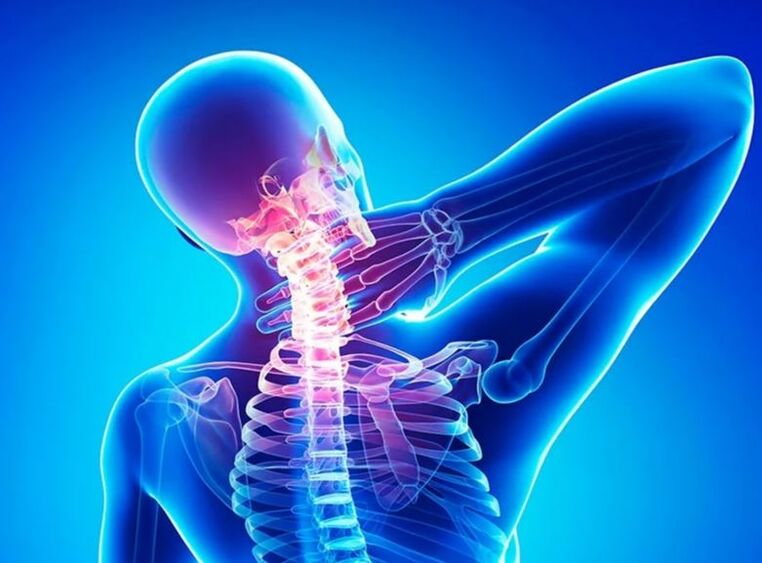
Description of the disease
Osteocartilage degeneration is the pathological state of spinal bone marrow tissue.The disease is characterized by changes in malnutrition and a decrease in disc absorption function.Pathology promotes deterioration of spinal fixation capacity due to reduced disc height and lower tone of vertebral muscles and ligaments.
Depend on the localization of changes in malnutrition: cervical spine, chest, waist, and s bones, distinguish several forms of osteochondral disease.One of the most common is cervical osteochondrosis (25% of the total).The disease is accompanied by an unpleasant feeling that can significantly reduce the quality of human life.
It is worth noting that cervical osteocartilage may occur at any age.Currently, the disease is often diagnosed even among school children and students, which is associated with a sedentary lifestyle and long-term stay in computers and textbooks (depend on the wrong position of the body).
Without treatment, osteocartilage will progress, symptoms become more obvious, and complications often occur: disc hernia, nerve pinch, circulation, hypoxia, etc.
symptom
As the skeletal cells of the cervical bone cartilage bone feel, the intervertebral discs in the cervical vertebra are insufficient in nutrition, and they become brittle, and the distance between them is greatly reduced.At the same time, bone tissue is prone to the growth and formation of bone growth (bone plants).In later stages, growth moves and begins to squeeze nearby tissues, blood vessels and nerves occur in the cervical area.
Neck bone and chondropathy- Chronic, gradually developing disease.Therefore, the pathological symptoms are different at different stages.
- Symptoms of first-grade osteochondrosis
During the initial stages of the disease, the disc height of the cervical spine drops slightly.The pathology has mild symptoms.If you have discomfort on your neck, you can spread it on your shoulders.In some cases, neck pain may occur during physical exercise. - Symptoms of secondary osteochondral bone marrow disease
At this stage, the height of the disk continues to decrease, the cartilage tissue is incorrect, and the protrusion occurs.Cracks can be formed in the fibrous annex.The pain begins to intensify, grows longer, and can radiate to the hands and spine.The neck turns, tightening and headaches are possible for stiffness. - Symptoms of third degree osteochondrosis
In the third stage of the disease, annular fibrous fibrous fracture and vertebral hernia formation.The spine is deformed, and vertebrae dislocation or subluxation may occur.The patient will experience acute, prolonged pain in the neck, numbness, partial loss of sensitivity in the skin area of the neck, neck, shoulders or hands. - Symptoms of fourth degree osteochondrosis
In the late stages of the disease, irreversible changes occur - many bone plants occur, and the structure of the intervertebral disc is gradually replaced by scar fabrics.The resulting hernia pressure is on the blood vessels and nerves, and a person suffers from organ hypoxia, the pathology of the circulatory system.The pain lasts for a long time, the neck and upper shoulder straps become fixed, and the quality of life is greatly deteriorated.
Regardless of the severity of the disease, patients can experience symptoms such as ear headaches, noise or sound, nausea, various visual impairments (flashing, darkening, pain).
reason
Cervical osteochondrosis occurs due to improper distribution of the cervical spine.At the same time, the neck muscles are unable to cope with mechanical stress, spasms, which can lead to circulatory diseases.As a result, changes in the upper spine.
Factors that contribute to the development of cervical osteochondrosis:
- Genetic tendency;
- Neck injury;
- A sedentary lifestyle;
- Stay in one position for a long time - in computers, driving, etc.;
- The presence of autoimmune diseases is rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus,
- scleroderma;
- Invasion of metabolism;
- The presence of endocrine diseases - gout, diabetes;
- Too big.
diagnosis
If cervical osteochondrosis is suspected, it is necessary to contact the medical institution in a timely manner.A comprehensive diagnosis will help determine the disease, assess its degree and understand the causes of pathological development.A preliminary diagnosis was made based on examination and palpation - osteochondrosis, the tension of the cervical spine will be noticed, and in some cases, deformation of the spine is worth noting.
After objective diagnosis, the doctor sent the patient to other studies.
The following diagnostic methods are used to confirm the diagnosis:
- Magnetic resonance tomography;
- X-ray (lateral and straight);
- Multi-layer computed tomography scan.
To determine the cause of pathological development, an additional prescription can be given to perform ultrasound examinations on nearby organs, electrocardiograms, double-strand scans of blood vessels, blood tests and urine.
treat
By promptly detecting cervical osteochondrosis, this disease is very suitable for treatment.Unfortunately, osteochondrosis cannot be completely cured, but treatment will help prevent further development of the disease, alleviate unpleasant symptoms and normalize the upper spine mobility.
The following methods are used for this:
- Drug treatment.The medication reduces pain and inflammation, restores blood circulation and eliminates cramps in the neck muscles.To do this, the following drugs can be used: glucocorticoids, analgesics, slow medications, muscle relaxants, etc.
- Physical therapy.In addition to taking medications to relax cervical muscles, eliminating cramps and normalizing blood circulation can also help with physical therapy procedures: massage, acupuncture, laser effects, magnetic therapy, UHF therapy, UHF therapy, voice therapy, and more.
- Treatment gymnastics.Special body movements will help patients strengthen the muscle frame, align posture and improve blood supply to the upper part of the spine.
Surgical treatment
If the late stages of cervical osteochondrosis or the effectiveness of the conservative approach is insufficient, surgery is required.
The following surgical methods can be used according to specific clinical conditions:
- A small invasive removal of vertebral hernia.
- Laminectomy is the procedure for removing the vertebrae.
- A system consisting of four titanium screws and two rod peaks removes the hernia and stabilizes the operating segment.
- Endoscope clears hernia.