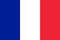
Causes of low back pain
Muscle and ligament injuries
herniated disc
Intervertebral disc degeneration and aging (osteochondrosis)
Spondyloarthropathy (osteoarthrosis of the intervertebral joints)
spinal stenosis
Spondylolysis
osteoporosis
pressure
other factors
- bone-destroying infection (osteomyelitis),
- malignant oncology, especially if metastases occur to the spinal bones,
- Psoriasis, especially arthritis,
- Fibromyalgia.
- urinary tract infection,
- Diseases of the abdominal organs, kidneys and pelvic organs.
Postural problems
low back pain during pregnancy
Types of feeling in lower back pain
- Severe, burning, sharp, almost unbearable pain. Typical manifestations are hernia, radiculitis, and lumbago (low back pain).
- Dull, aching, popping or aching pain. It usually occurs due to injury, inflammation or muscle strain, or problems with the soft tissue surrounding the spine.
- Chronic pain can have different qualities; it often intensifies into burning, aching, or tingling sensations with movement or uncomfortable positions. They weaken when resting, wearing corsets, or assuming certain body positions.
Diagnosis of low back pain
- A set of laboratory tests that rule out inflammatory processes and pathologies of internal organs.
- X-ray of the spine (usually in two projections: direct and lateral). This helps identify skeletal abnormalities, vertebral and joint deformities.
- Computed optical topography of the spine can assess postural disorders and determine the degree of spinal deformation and pelvic distortion.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is the most common and informative method for diagnosing spinal conditions. MRI can detect damage to discs, joints, spinal cord, vertebrae, and other structures.
- ENMG (electromyography) – assesses neuromuscular transmission status, nerve and muscle function.
Treat lumbar pain
- Pain relievers, decongestants and anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants and vitamins (tablets, ointments, injections, droppers);
- Physiotherapy techniques (intratoplasmic electrical stimulation, carboxyl and ozone therapy, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy, amplified pulse therapy);
- Kinesio tape,
- massage, manual therapy and osteopathy;
- acupuncture;
- Physical therapy and other methods.