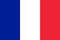
What does lower back pain look like?
Why does my lower back hurt?
Musculoskeletal disorders that cause lower back pain
Muscle and ligament deformations and sprains

spinal injury
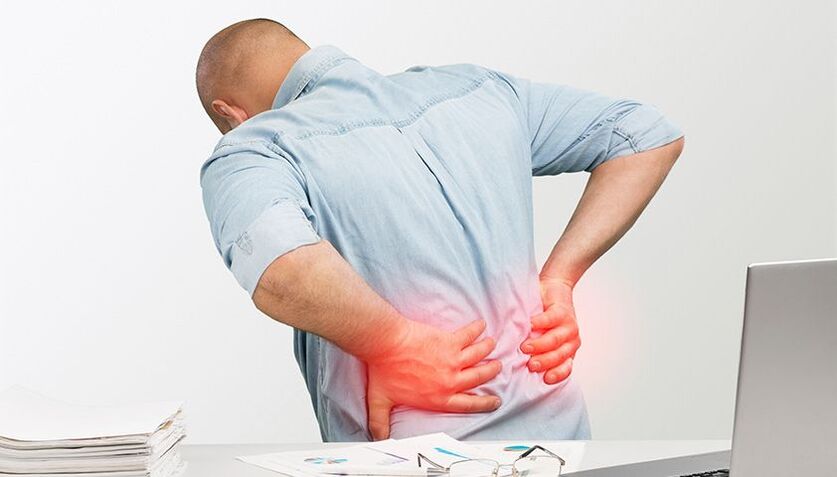
Intervertebral disc pathology
lumbar scoliosis
Arthritis and joint disease
spondylolisthesis
spinal infectious diseases
Spinal tumor disease

Internal organ diseases causing lower back pain
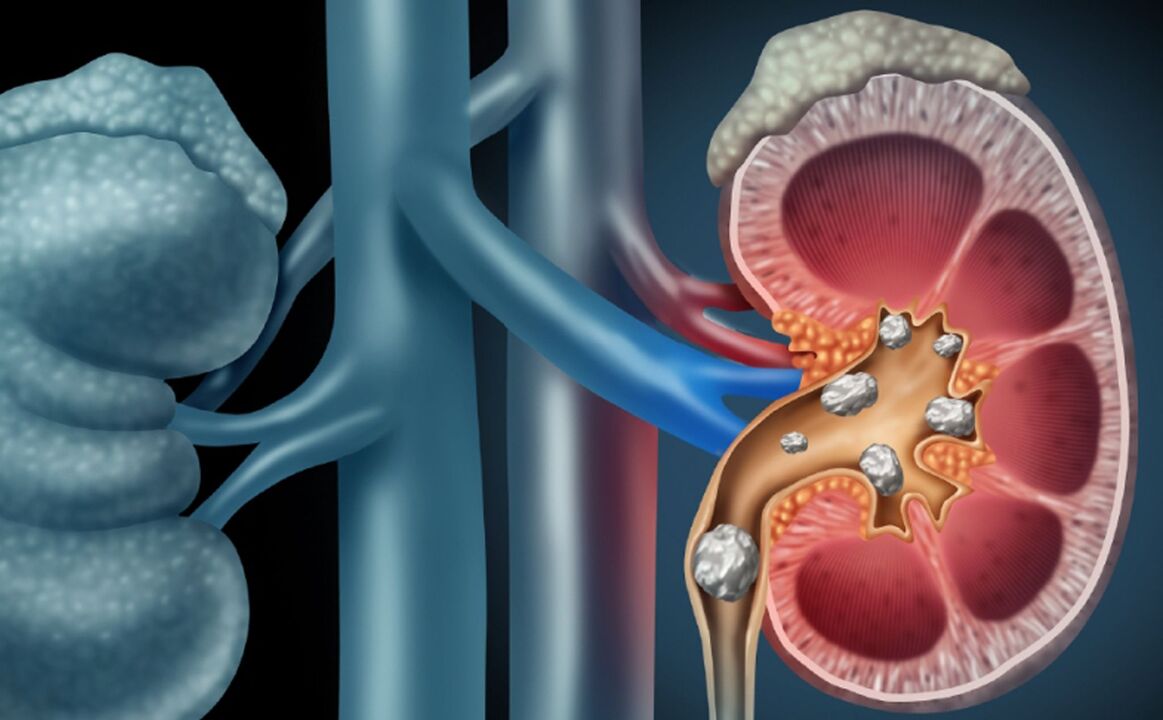
urolithiasis disease
abdominal aortic aneurysm
How to prevent low back pain
- A varied diet that includes the vitamins and minerals needed to maintain healthy bones, muscle tissue, and joints;
- maintain a healthy weight;
- Engage in regular physical activity: Exercise to prevent low back pain should include strength exercises to strengthen the muscle frame, stretches to relieve muscle tension and spasms, and aerobic exercise to maintain blood supply and tissue nutrition;
- Follow safety precautions when exercising - for example, first classes in the gym must be supervised by a qualified instructor;
- Follow safety precautions at home - Many injuries can be avoided if you wear comfortable shoes, hold onto railings on stairs, and take your time when it's slippery outside;
- Observe safety precautions when lifting heavy objects - if you get as close to the object as possible (without reaching for it), the load on your spine will be less, and when lifting objects from the floor, bend your legs instead of leaning your body.